AI at the Edge, Pasta Detection Demo with AWS
Amazon Web Services
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is the world’s most comprehensive and broadly adopted cloud platform, offering over 165 fully-featured services from data centers globally. Millions of customers - including the fastest-growing startups, largest enterprises, and leading government agencies — trust AWS to power their infrastructure, become more agile, and lower costs.
AI at the Edge Pasta Detection
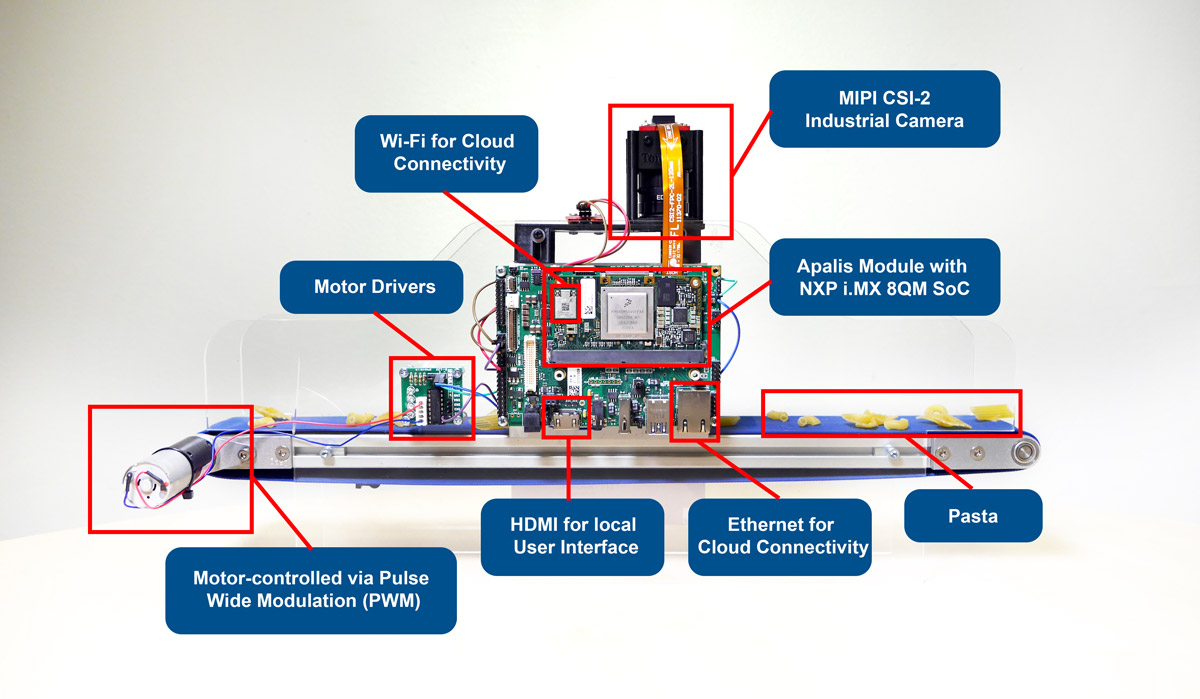
This is a computer vision demonstration that integrates several technologies to showcase an edge computing scenario that involves the detection of pasta using artificial intelligence technology - deep learning, and the visualization of live and historic data processing both on a cloud dashboard, using cloud services from Amazon Web Services, as well as a local graphical user interface (GUI), using a GUI framework that relies on modern web technologies.
Here is a brief technical overview of the technologies used:
- An industrial MIPI-CSI2 camera to capture a video stream from the conveyor belt.
- Deep learning inference running on the Apalis iMX8 at the edge, using the DLR inference engine.
- Neural Network trained using Amazon SageMaker and optimized for performance using Amazon SageMaker Neo.
- Employs Single Shot Detector (SSD) algorithm for object detection
- MobileNet SSD v1 neural network architecture
- Example dataset containing pasta images and annotation files is provided in Pascal VOC format
- A local GUI on the HDMI video output built with the Quasar Framework, displaying live pasta detection.
- A web dashboard to display historic data, built using several connected AWS services:
- AWS IoT Greengrass for MQTT data ingestion and relaying to other AWS services.
- Amazon DynamoDB for data storage.
- Amazon Cognito for secure user management.
- Amazon CloudFront for web dashboard hosting.
See below an illustration of how the AI at the Edge Pasta Detection demonstration integrates the AWS services:
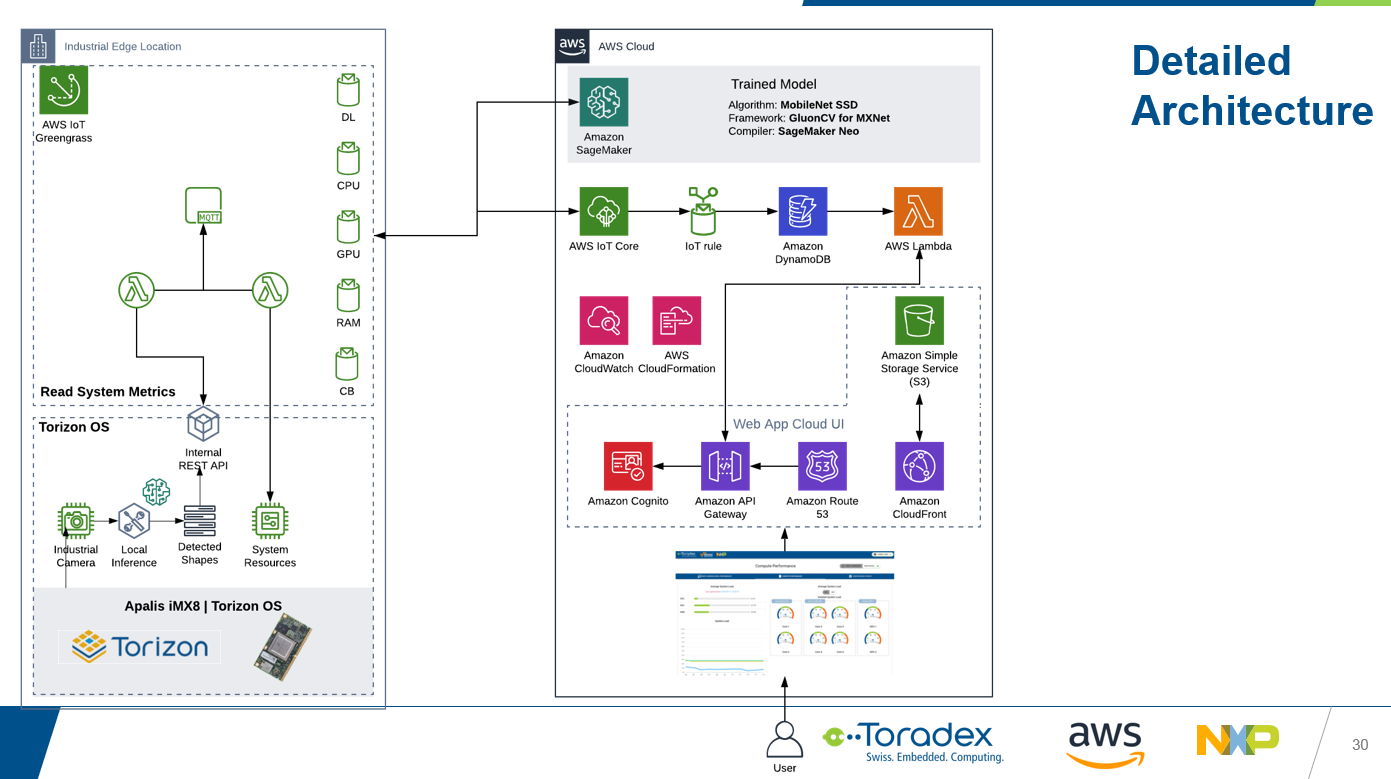
AWS IoT Greengrass
AWS IoT Greengrass extends AWS to edge devices so they can act locally on the data they generate, while still using the cloud for management, analytics, and durable storage. With AWS IoT Greengrass, connected devices can run AWS Lambda functions, execute predictions based on machine learning models, keep device data in sync, and communicate with other devices securely – even when not connected to the Internet.
In the context of this demo, AWS IoT Greengrass provides a seamless, secure, and resilient connection to the cloud. System data such as the deep learning inference results and the overall system status are collected, pre-processed, and sent to an MQTT broker. At the same time, commands to control the conveyor belt and the LED brightness are received from the web dashboard, providing two-way communication between device and cloud.
Amazon SageMaker Neo
Amazon SageMaker Neo enables developers to train machine learning models once and run them anywhere in the cloud and at the edge. Amazon SageMaker Neo optimizes models to run up to twice as fast, with less than a tenth of the memory footprint, with no accuracy loss.
Amazon SageMaker is used to train a deep learning inference model from a pasta dataset, focusing on object detection and using the MobileNet SSDv1 algorithm, while Amazon SageMaker Neo then optimizes the trained model for the NXP i.MX 8QuadMax processor, which is the core of Toradex Apalis iMX8.
Supported Modules
The following Computer on Module is supported:
Supported Displays
- HDMI video output from the Ixora Carrier Board only.
Intended Use
This partner demo image is meant for the evaluation of the technology and as a starting point for your project. It is not suitable for production.
Prerequisites
- An Apalis iMX8 Embedded Vision Kit with Allied Vision. If you don't have the kit, you can get the parts independently:
- An Ethernet Cable to connect the board to your local network, with access to the external internet.
- A USB mouse and keyboard, for installing the demo on the Apalis iMX8 internal memory.
- HDMI Monitor
- Specific types of pasta. The reference numbers are from Barilla, but you are free to try out similar pasta from other brands:
- Medium Shells - N. 393
- Elbows - N. 41
- Mini Penne - N. 366
- Farfalle - N. 65
Optional Items
The Apalis iMX8 Embedded Vision Kit with Allied Vision does not contain the mechanical parts and accessories to assemble the full demo as showcased by Toradex, NXP, and AWS in tradeshows and events. These items are not mandatory to have the functional demo running. However, you can source or manufacture the components by yourself, and then assemble the full demo:
- Conveyor belt type 20 miniature from AS Conveyor Systems:
- Width: 60mm; length: 500mm; speed: 27m/min
- Plexi plastic mounting structure design, to manufacture:
- 3W high-brightness LED
- Motor driver based on the ULN2003 integrated circuit
- 3D printed enclosing for the camera and LED, to manufacture:
- 3D print design file
- Female/Female Jumper Wires
How to Get Started
This section provides instructions for you to get started with the AI at the Edge Pasta Detection demo.
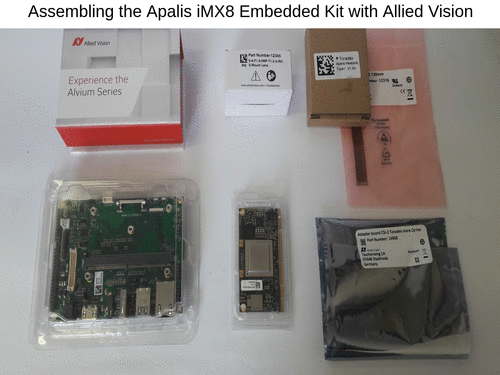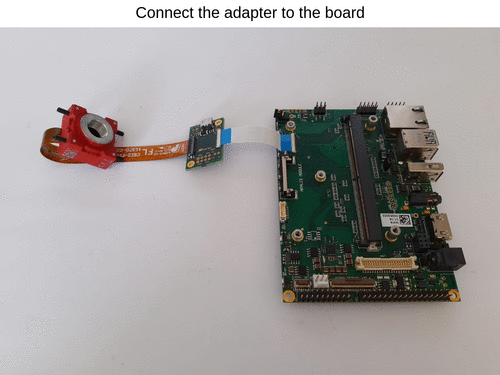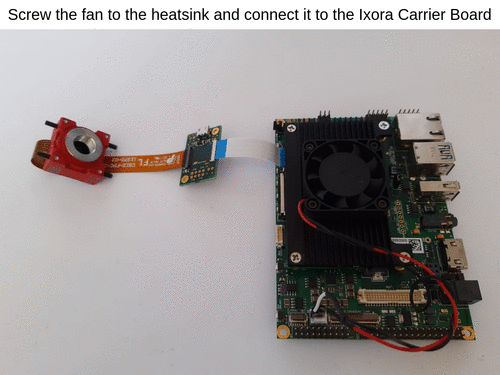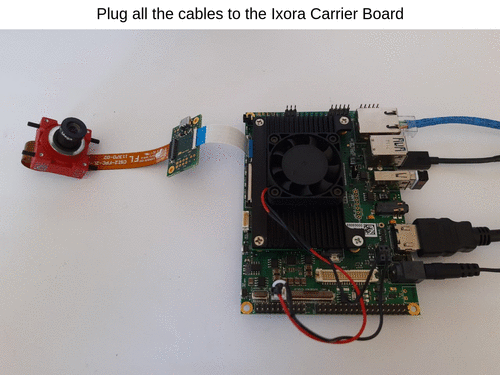
Assemble the Apalis iMX8 Embedded Vision Kit with Allied Vision
To assemble the kit only, follow the instructions enumerated and illustrated by the gif below:
- Unbox all items.
- Connect the camera to the adapter.
- Connect the adapter to the board.
- Connect the Apalis iMX8 to the Ixora Carrier Board.
- Make sure that the Apalis iMX8 is locked and well connected.
- Mount the Apalis heatsink on top of the module and fasten with screws.
- Screw the lens to the camera.
- Remove the lens protection.
- Plug all cables to the Ixora Carrier Board - HDMI, Ethernet, USB mouse / keyboard, power supply barrel jack.
Optional - Connect the DC Motor Driver and 3W LED to Ixora
We do not yet provide instructions for the mechanical assembly of the conveyor belt - which consists of the optional items described in the Prerequisites section. We do provide instructions on how to make the electric connections to the Ixora Carrier Board.
Before you continue, check if everything is fixed and the acrylic is stable. Make sure you have a jumper short-circuiting the driver's on/off pins.
- Use jumpers to connect motor driver ULN2003 pins 1, 5 to the motor.
- Connect driver + to Ixora's X4 pin 5, and driver - to Ixora's X4 pin 4.
- Connect driver's pin IN1 to Ixora X27 pin 33.
- Use jumpers to connect LED pins 1,2,3 to Ixora's X27 pins 32,31,34 respectively.
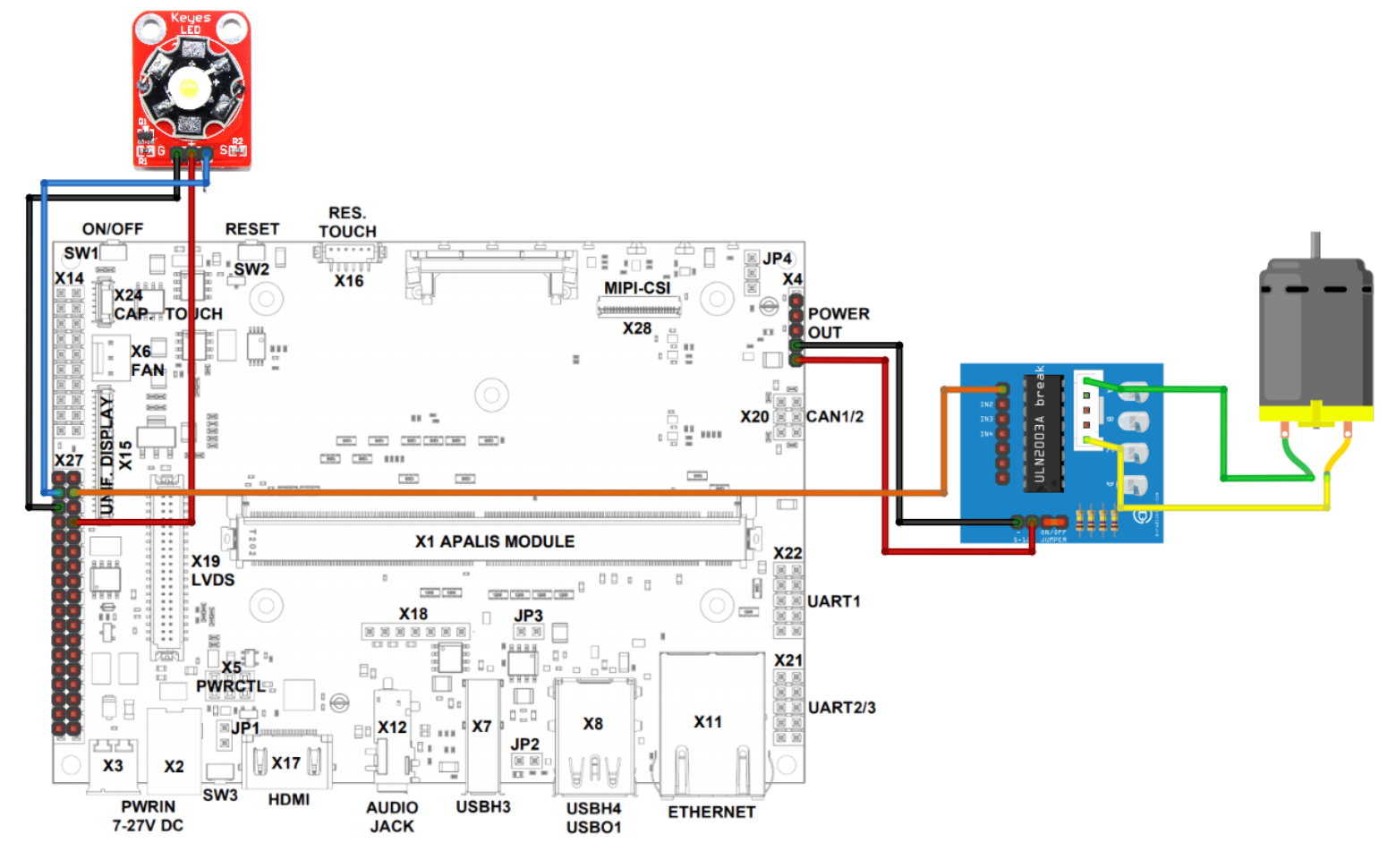
Install the Local User Interface
Power on the system. Toradex Easy Installer comes pre-installed and will be displayed on the HDMI interface:
Your module should have come with the Toradex Easy Installer pre-installed. If this isn't the case, you can easily follow the Loading Toradex Easy Installer article before proceeding.
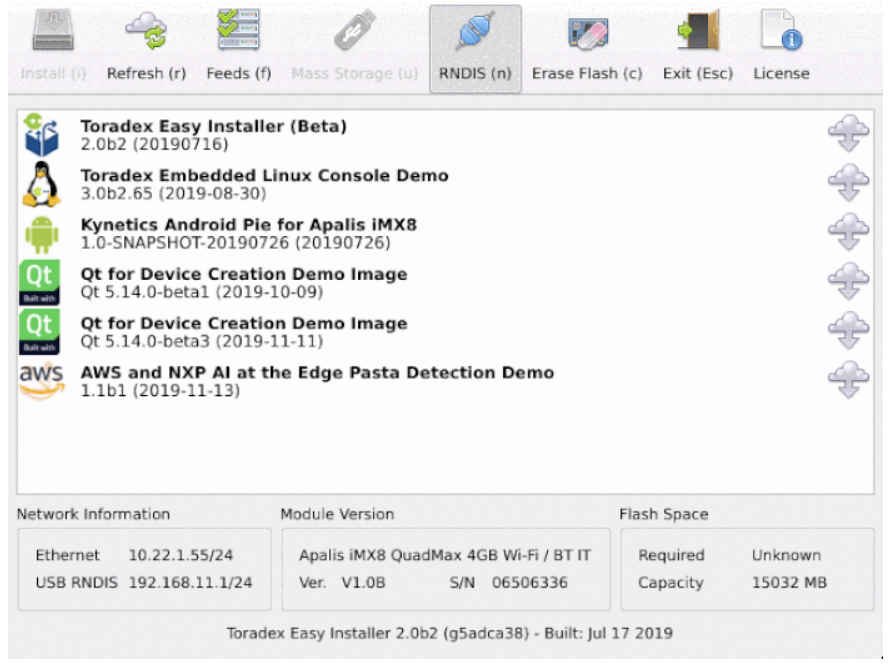
Do the following:
- Write down the Ethernet IP from Network Information.
- Write down the unique Serial number from Module Version.
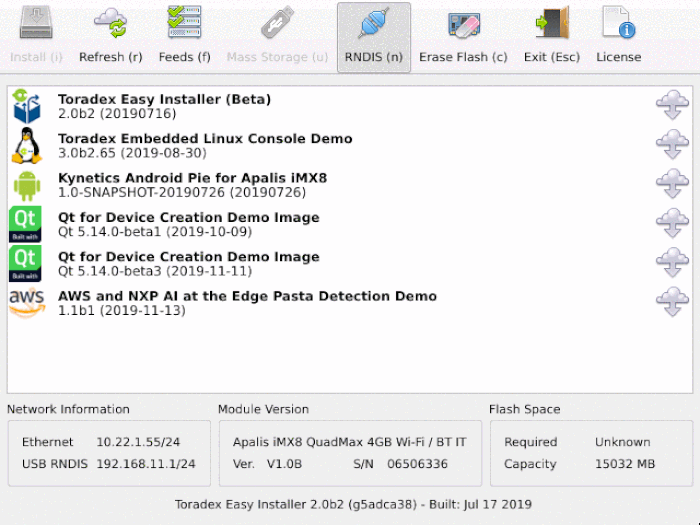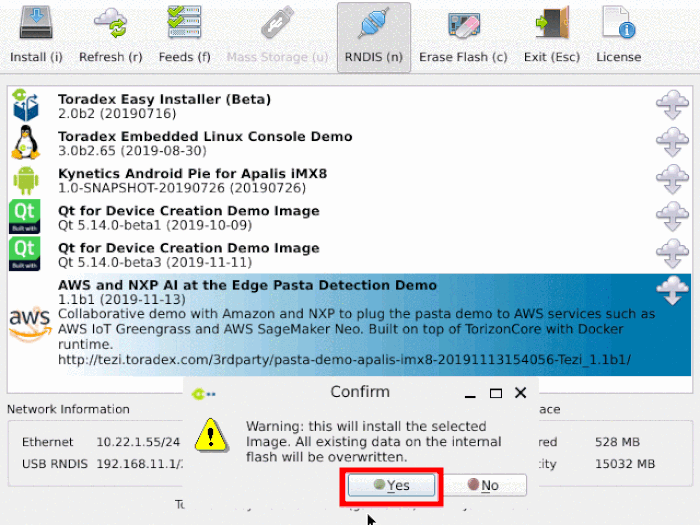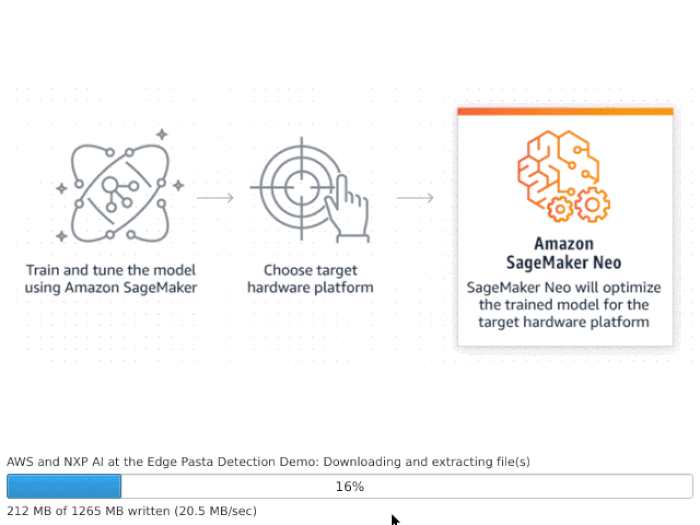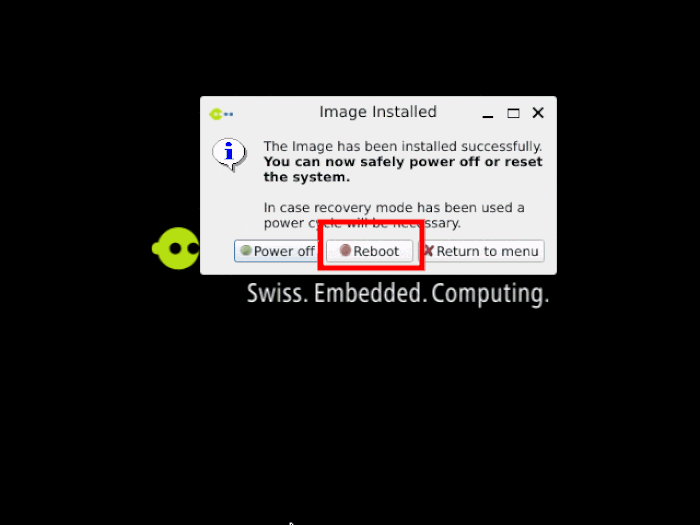
- Select AWS and NXP AI at the Edge Pasta Detection Demo image from the list and install it.
After the installation and reboot, you will see at the HDMI display the welcome screen.

It may take 5 minutes or more for the demo to start. It happens because Docker containers are fetched online after the first boot. After the containers are downloaded and started you can see some inferences in the local user interface.
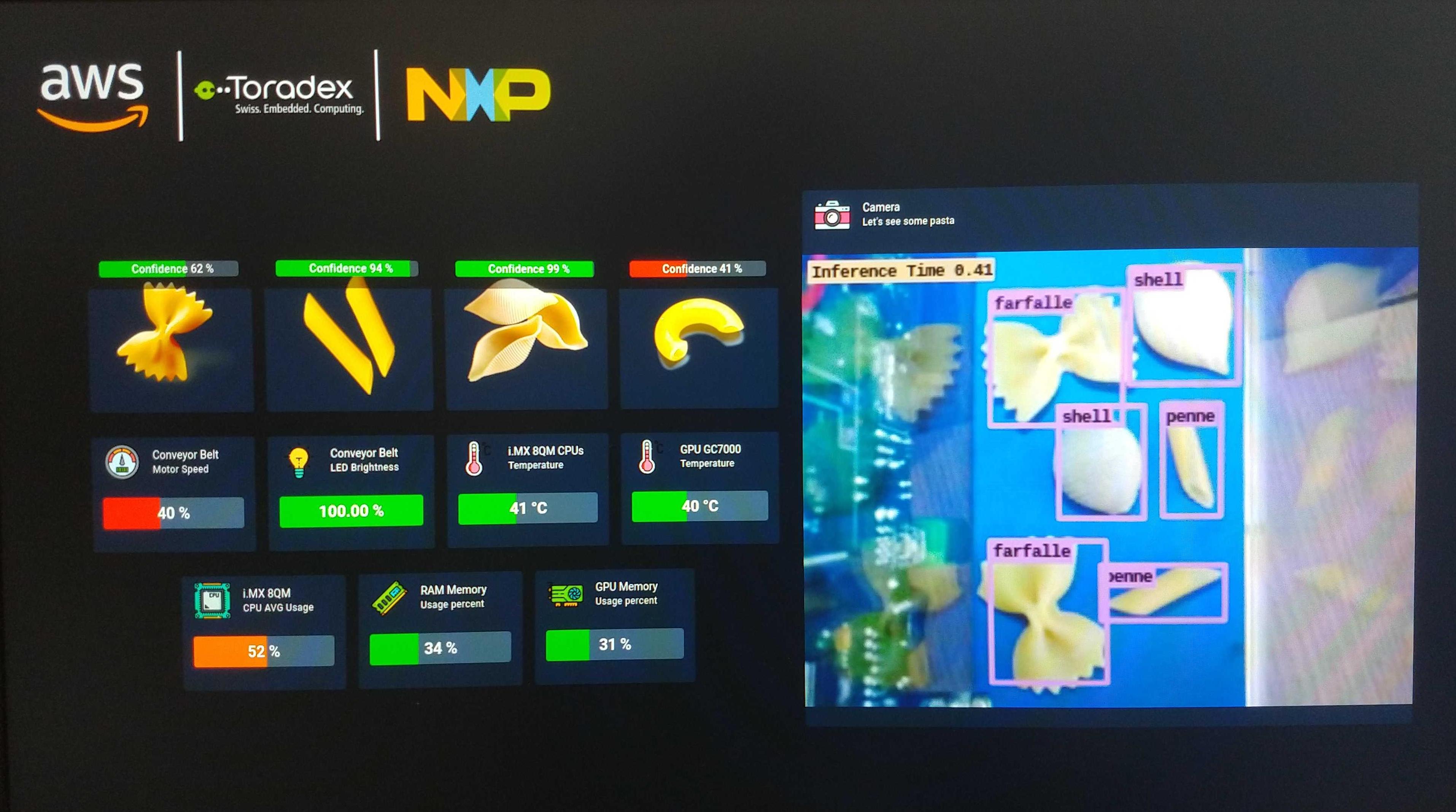
Now you can test the local user interface with some pasta.
Connect the Demo to Cloud
This section provides instructions to set up the connect your board to your AWS account.
Create an AWS Account and User Access Key
Follow AWS page instructions to create a new AWS account.
Once you have access to the account, create a user access key. Follow the instructions on the article Managing Access Keys for Your AWS Account Root User to understand how to create it. You will create the access key ID and secret access key as a set.
Make sure to download your AWS credentials to your local machine, which will be used for future reference, by clicking on the "Download Key File" button.
if you have just registered and this is a fresh AWS account, some services are not available before AWS validates your account which can take up to 24 hours.
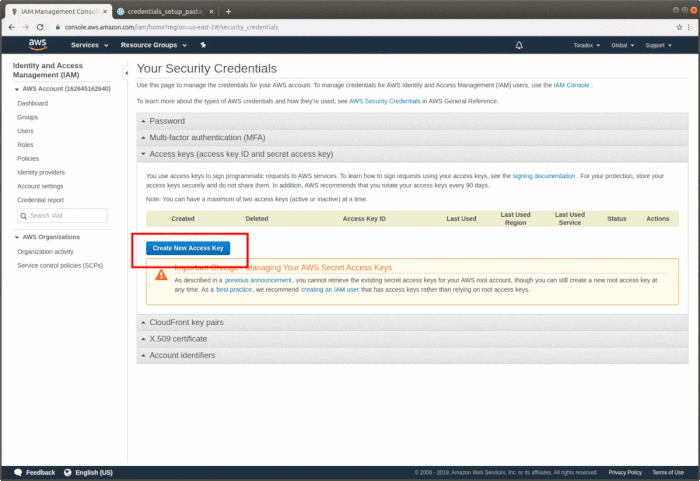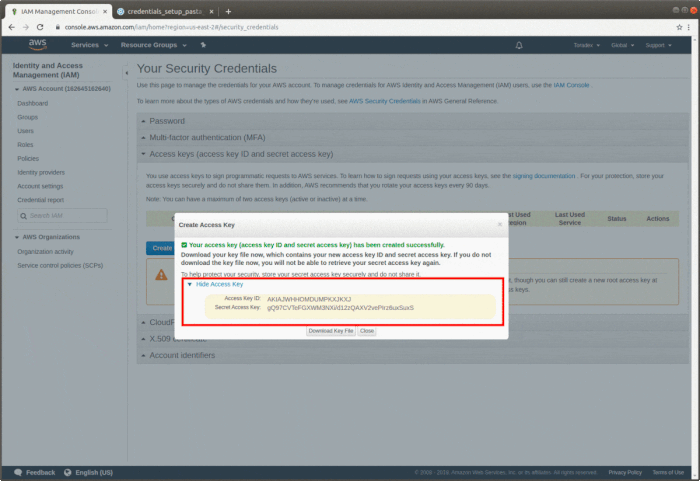
During access key creation, AWS gives you only one opportunity to view and download the secret access key part of the access key. If you miss or lose it, you will need to create a new access key.
Connect Your Device
When you installed the demo image using the Toradex Easy Installer, you were instructed to write down the serial number and the Ethernet IP. You will select one of them to access a web-based user interface to easily create the cloud infrastructure directly from the Computer on Module.
On a desktop PC connected to the same network as the Computer on Module, open a web-browser (for example Chrome or Firefox) and use either one of the following URLs:
-
http://<Board's Ethernet IP>:8080or
-
http://apalis-imx8-<serial number>.local:8080
See the example below for my Apalis iMX8, with Ethernet IP 192.168.10.5 and serial number 0333444555. The zero to the left cannot be disregarded:
-
http://192.168.10.5:8080or
-
http://apalis-imx8-0333444555.local:8080
Which method should I use
Both methods have pros and cons. They are weighted with a default domestic network configuration in mind.
If you know the IP address of the board, the Ethernet IP address method is more reliable, since your local DNS server does not need to resolve the hostname.
If the local DNS resolution works well in your network configuration, the serial number is deterministic, since it will never change, while an IP address assigned by your local DHCP server is susceptible to changes over time.
You will see the following screen:
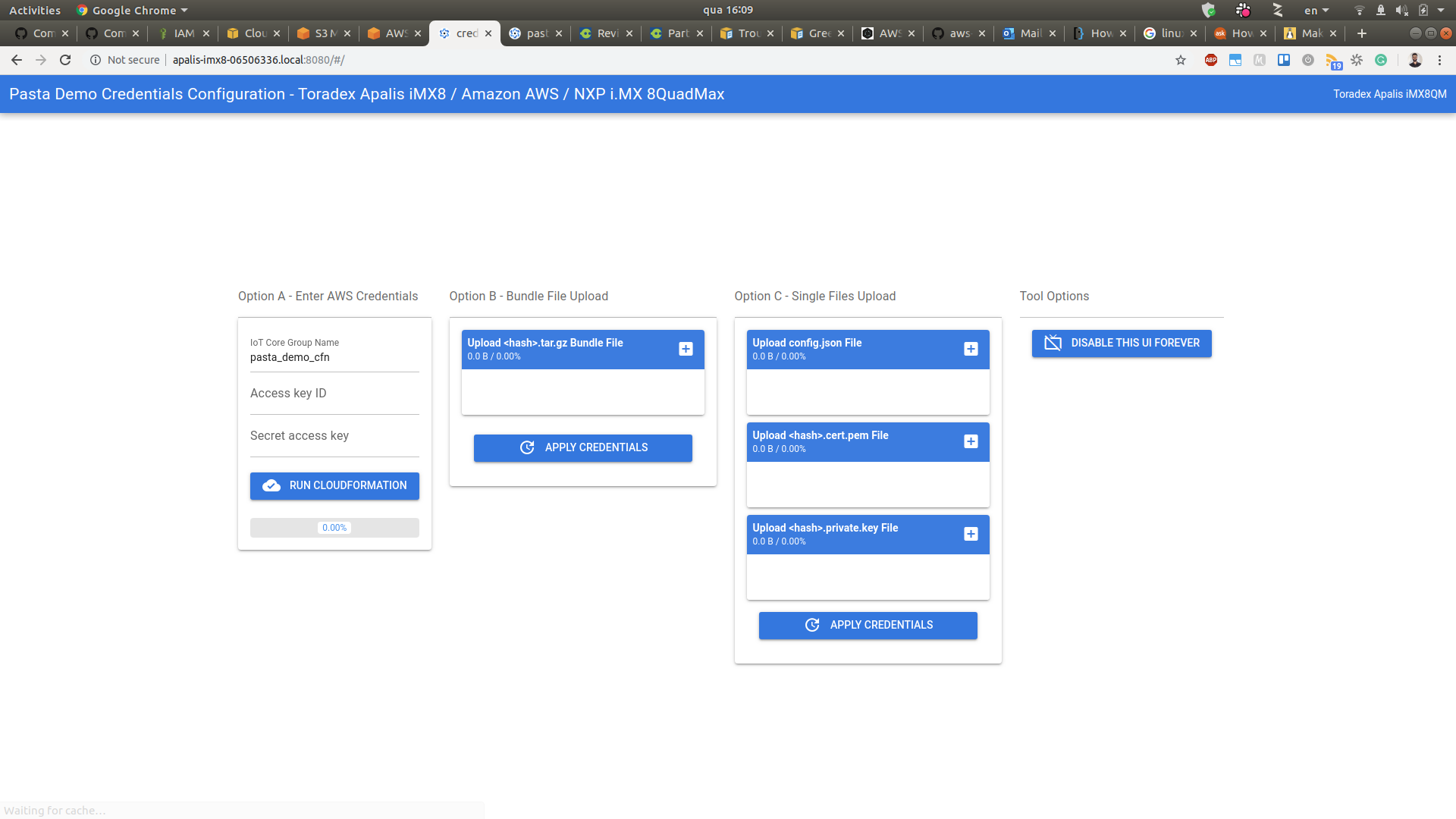
the browser may mark the website as not secure.
Create the Cloud Infrastructure
Fill the access key ID and secret access key created previously and hit the Run CloudFormation button. It will deploy the entire AWS infrastructure required to run the demonstration.
this step can take around 15 minutes to 1 hour since Amazon CloudFront needs time to register the internet domains. Now is the perfect time to go grab a cup of coffee.
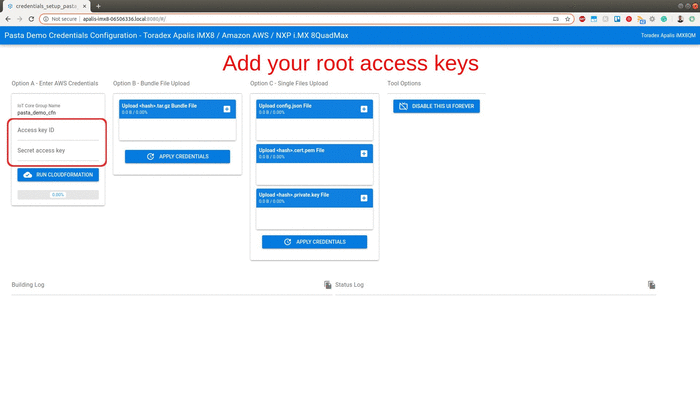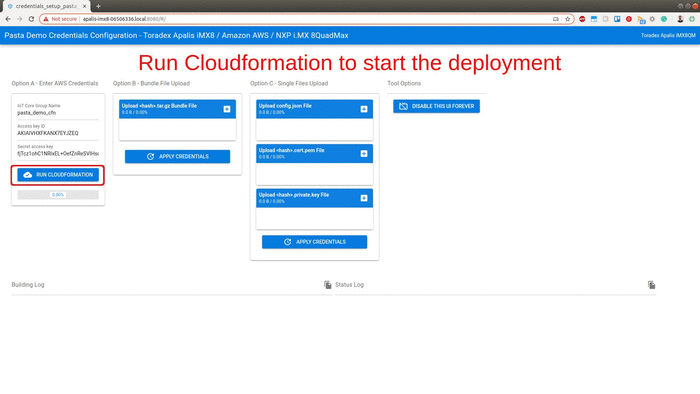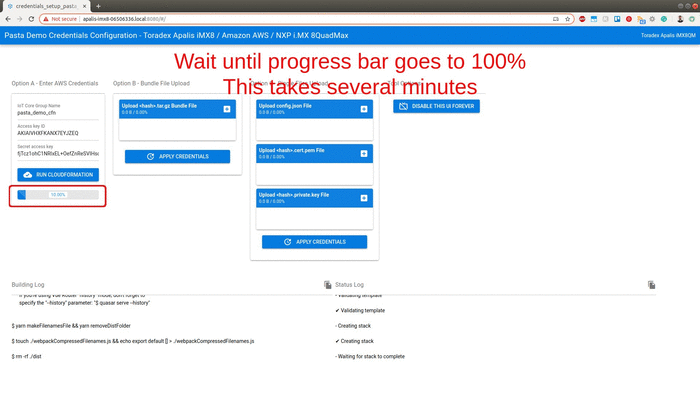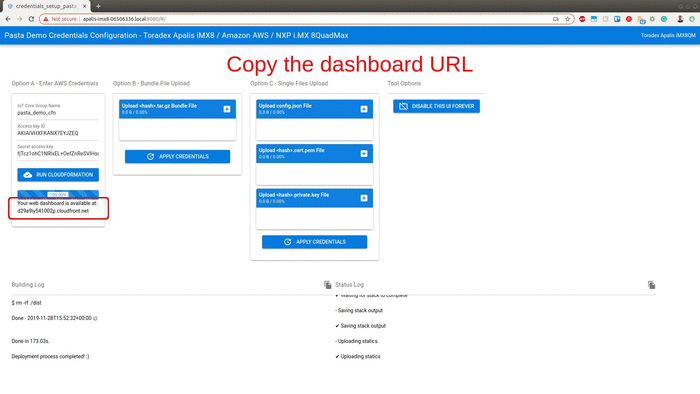
Once the progress bar hits 100%, the full deployment is finished. Within seconds your board will start sending data to your dashboard. Copy the URL for your own dashboard as illustrated in the gif above.
Access the Web Dashboard
Use the URL retrieved above to access, sign-up and sign-in to your web dashboard:
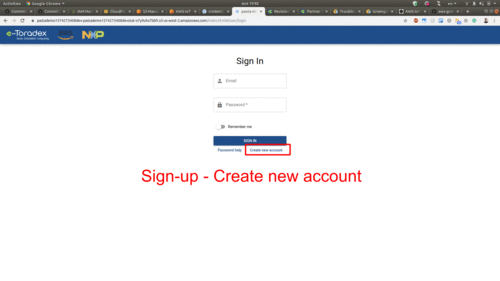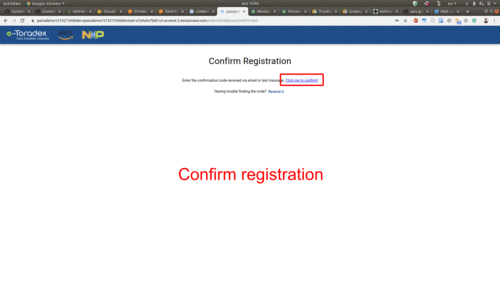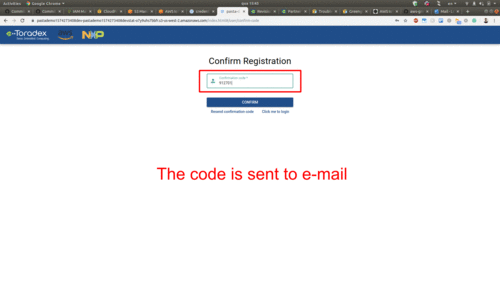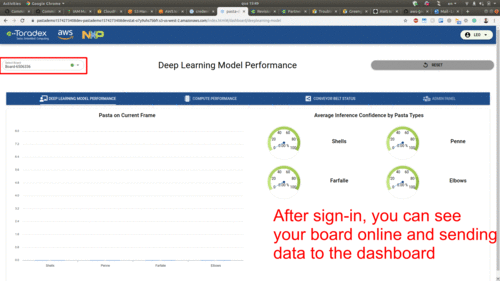
Play With the Pasta Demo
Put some pasta under the camera and see it reflect on the local user-interface and the web dashboard.
Next Steps
The AI at the Edge Pasta Detection demo is open-source. Notice that it is provided as-is.
Train an Object Detection Algorithm
- Please read Train a Neural Network for Object Detection algorithm (SSD) for iMX8 boards using SageMaker Neo.
- The generic development steps to deploy the model would be to follow the article Executing models tuned by SageMaker Neo in a Docker Container using DLR runtime, Gstreamer and OpenCV. In this demo, you will actually have to replace the model in the container_inference source code available on the Pasta Demo repository aws-nxp-ai-at-the-edge on GitHub.
Modify the Demo Containers and AWS Cloud Structure
You can tweak the demo in several ways, from the web UI to the inference model and much more. Here are the public GitHub repositories and additional resources:
| GitHub Repository | Description | Additional Resources |
|---|---|---|
| aws-nxp-ai-at-the-edge | AWS Lambdas, containers, inference application, etc | - |
| aws-nxp-ai-at-the-edge-gui | Local graphical user interface (GUI) that outputs on HDMI | - |
| aws-nxp-ai-at-the-edge-credentials-setup | Tool to add AWS IoT Greengrass Core device credentials and set up the cloud infrastructure to a fresh setup hardware | - |
| meta-pasta-demo | Yocto layer to re-build and/or customize the Linux image | Instructions how to re-build the Linux image on Build the AWS AI at the Edge Demo Image |
| aws-nxp-ai-at-the-edge-cloud-dashboard | Cloud dashboard interface GUI and infrastructure | - |
| Alvium device driver | Device driver for the Alvium camera provided by Allied Vision | - |
Release Notes
2.0.0
Release: https://github.com/toradex/meta-pasta-demo/releases/tag/v2.0.0
- Add support for the Allied Vision Alvium C-500c camera
- Drop support for the Toradex CSI Camera Module 5MP OV5640
1.0.1
Release: https://github.com/toradex/meta-pasta-demo/releases/tag/v1.0.1
- Add splash screen
- Bug fixes
1.0.0
Release: https://github.com/toradex/meta-pasta-demo/releases/tag/v1.0.0
- Initial Release
Downloads
Download offline installers and older releases of the Partner Demo Image in this section.
2.0.0
1.0.1
1.0.0
Troubleshooting
Here are some tips to help you troubleshoot issues with the demo.
Debug Interfaces
To check if all the services are running correctly you need to have access to the Torizon bash on the board. There are two ways to access it from another machine (a.k.a host machine):
Debug UART (Serial)
The Apalis iMX8 Embedded Vision Kit with Allied Vision comes with all cables needed to connect to the debug UART. Follow the instructions on Configuring Serial Port Debug Console (Linux/U-Boot) to attach the hardware and connect.
SSH
To connect to the board via SSH, follow the Quickstart Guide until you reach the lesson Linux Terminal and Basic Usage.
Demo Does Not Start
the first boot, after installation, can take a long time (usually more than 15 minutes).
The boot may take 5 minutes or more for the demo to start. It happens because Docker containers are fetched online after the first boot. After the containers are downloaded and started you can see some inferences in the local user interface.
But if the demo takes longer than normal to start and is hang on this screen:

Access the board Torizon bash and follow the steps below:
Systemd Units
Make sure you are running the commands in the Torizon bash on the board. Use the password that was added during the first boot after installation for super user commands sudo.
Check if the demo services are ok with the command below:
systemctl status local-ui.service system-control.service system-status.service
All services must be active and with a green mark:
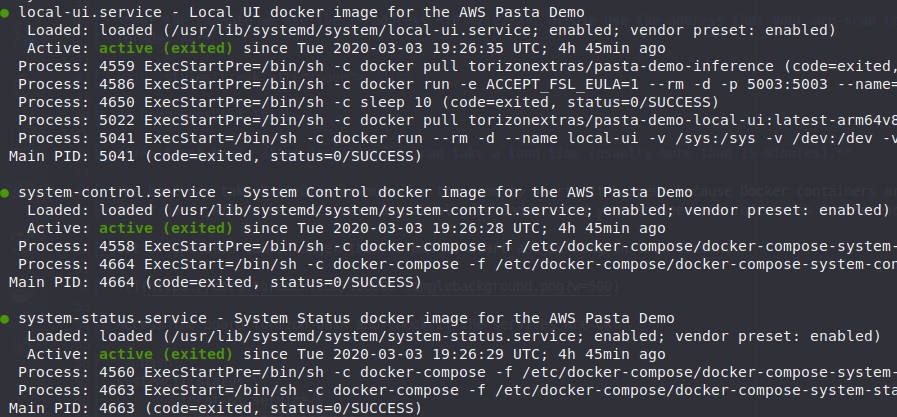
If the services are ok, move to the section Docker Containers
If any service has warnings or errors try restarting the services with the command below:
sudo systemctl restart local-ui.service system-control.service system-status.service
If that still does not resolves the issue, take note of the logs returned by systemctl status to ask the Toradex team for help.
Docker Containers
make sure you are running the commands in the Torizon bash on the board. Use the password that was added during the first boot after installation for the superuser commands sudo.
Check if all the demo docker containers are running with the command below:
docker ps
This command should return the following containers (check Name collum):
- local-ui
- inference
- docker-compose_front-end_1
- docker-compose_back-end_1
- docker-compose_system-info_1
- docker-compose_system-control_1
If the docker ps command did not return all the containers name listed above, try restarting the services with the command below:
sudo systemctl restart local-ui.service system-control.service system-status.service
If that still does not resolves the issue take note of the container that is not going up to ask the Toradex team for help.
Black Screen
If after booting you get only a black screen and nothing else try the following:
Make sure you are running the commands in the Torizon bash on the board. Use the password that was added during the first boot after installation for the superuser commands sudo.
- Check HDMI connection
- Access the Torizon bash:
- Check the weston service with the command below:
systemctl status weston
The service must be active and with a green mark:
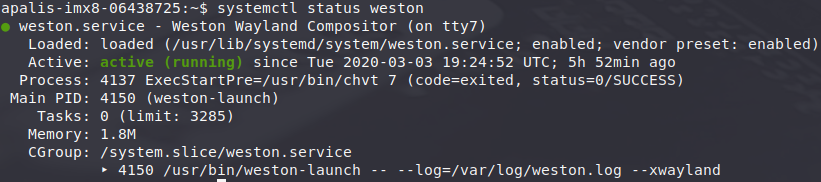
If the service has warnings or errors try restarting the service with the command below:
sudo systemctl restart weston
If that still does not resolves the issue, take note of the logs returned by systemctl status weston to ask the Toradex team for help.
Dashboard Not Receiving Data
If apparently the demo is running with no issues on the board but the online dashboard is still not receiving updated data from the inferences and system status, do the following:
Make sure you are running the commands in the Torizon bash on the board. Use the password that was added during the first boot after installation for super user commands sudo.
- Check the ethernet cable
- Access the Torizon bash
- Make sure the board has an internet connection. Try to retrieve the Google page:
wget www.google.com && rm index.html
This command should download the 100% of the page without issues:
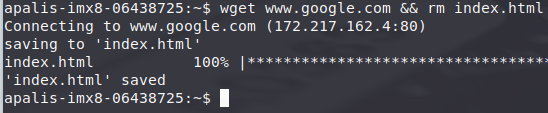
If you have an error or are unable to download the page you have problems with your network connection.
if you are sure that your network connection is working correctly but still cannot download the page on the board. Get the board dmesg logs and send to Toradex team:
dmesg > dmesg.log
Greengrass Service
Make sure you are running the commands in the Torizon bash on the board. Use the password that was added during the first boot after installation for the superuser commands sudo.
Check if the AWS Greengrass service are running with the command below:
systemctl status greengrass-software
The service must be active and with a green mark. If the service has warnings or errors try restarting the service with the command below:
sudo systemctl restart greengrass-software
If that still does not resolves the issue, take note of the logs returned by systemctl status greengrass-software to ask the Toradex team for help.
System Freeze
If a general failure occurs and the system freezes, perform a manual reset. Press the RESET button (SW2) from Toradex Ixora board: