Qt on Torizon OS
Qt 6 support is not yet fully released on Torizon 7.
While it may work, it is not guaranteed. You may want to use this feature on Torizon 6 until it becomes available.
Introduction
This article provides general information and instructions for Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs) development with Qt on Torizon OS.
Qt is a popular framework for developing (GUIs), that can be used on Toradex's Systems on Module and Torizon OS.
A detailed comparison between the recommended options for developing Graphical User Interfaces on Torizon OS can be seen in the GUI Overview article
There are available Qt Debian containers for Torizon OS, with hardware acceleration (for Qt5 and Qt6 on Torizon OS 6, and for Qt5 on Torizon OS 5). And also Qt6 C++ and Qt for Python - Pyside 2 (and some option of Qt6 for Python in the future) VSCode Torizon IDE Extension template templates, working out of the box.
This article complies with the Typographic Conventions for Torizon Documentation.
Prerequisites
- A Toradex System on Module with Torizon OS installed.
- An understanding of GUI Overview.
- Reading and understanding of Debian Containers for Torizon.
- Awareness about Torizon OS Containers Tags and Versioning.
- A configured build environment, as described in the Configure Build Environment for Torizon Containers article or in the Set up the Torizon IDE Extension Environment article for using the Qt C++ or Python templates for Torizon OS.
Qt Debian Containers for Torizon OS
As mentioned, there are Qt Debian containers available for Torizon OS. These containers work on top of Wayland, as explained in Debian Containers for Torizon, and come with Qt base libraries installed and ready to use, providing hardware acceleration (application running on the GPU instead of just the CPU, improving performance) for Qt applications.
On Torizon OS 6, hardware acceleration works for both Qt5 and Qt6. On Torizon OS 5 just with Qt5.
These containers provided by Toradex are called qt6-wayland, qt6-wayland-vivante (for the IMX8 modules, that use the Vivante GPU) and qt6-wayland-am62 (for AM62-based modules). They are minimal containers with Qt6 libraries, which you should use as the base for deploying your own Qt6 app. There are also the qt5-wayland, qt5-wayland-vivante and qt5-wayland-am62 containers for Qt5.
The qt6-wayland, qt6-wayland-vivante and qt6-wayland-am62 containers can be used in two ways:
With the VSCode Torizon IDE Extension, that provides ready-to-use C++ and Python (Pyside2 for now) templates, that offer an out-of-the-box experience on Toradex System on Modules, together with benefits for development and integration with other parts of the Torizon OS ecosystem.
Through the CLI (command line interface), which can provide you an out-of-the-box evaluation experience on Toradex System on Modules with the
qt6-wayland-examples(and variations) containers.
This ways and how to use them will be described in the next sections.
Qt C++ Template for Torizon OS
The VSCode Torizon IDE Extension provides a ready-to-use Qt6 C++ QML template, that offer an out-of-the-box experience on Toradex System on Modules (SoMs), together with other benefits for application development and integration with other parts of the Torizon OS ecosystem like TorizonCore Builder and Torizon Cloud.
To create and run a Qt6 C++ application follow the Torizon IDE Extension development workflow.
This template also provides integration with Qt Creator and Qt Design Studio, allowing you to also develop and debug your application on the Toradex SoM using Qt Creator and Qt Design Studio if you want.
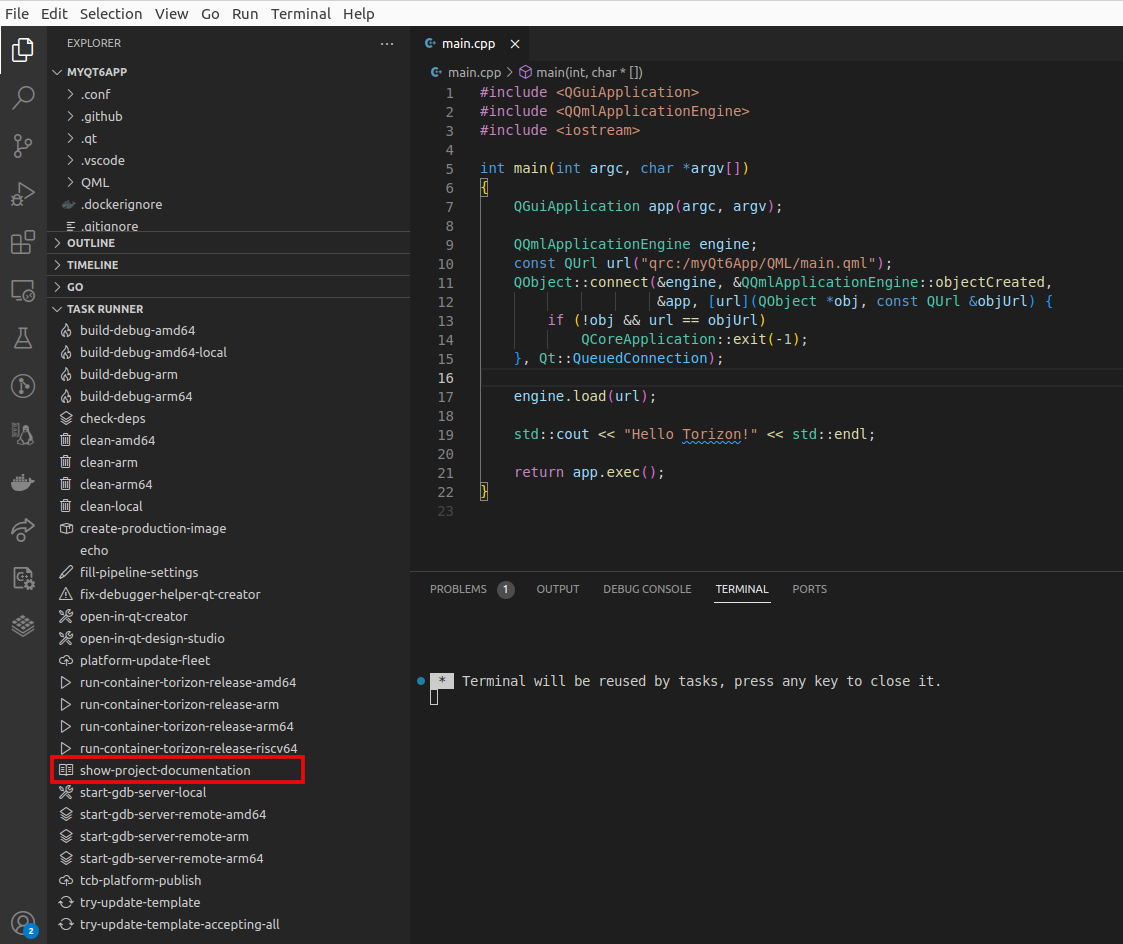
For the more details on how to do it check the template specific documentation. To do it, once you have created the project, click on the show-project-documentation task in the TASK RUNNER tab:
This template uses CMake as the build tool. But if you need to use qmake6 instead for some reason, it is possible to modify the template to use it. This commit can provide you some hints on how to do it (more specifically tasks.json, launch.json and where qmake6 is changed to cmake on the Dockerfiles).
As Qt5 has reached EOL on May 2023 and is currently on Extended LTS just for subscribers, it is highly recommended to use Qt6. However, as mentioned, there are also Qt5 containers for Torizon OS 6. So if you really need to use Qt5, you can eventually modify this Qt6 C++ template provided by the extension to use Qt5.
Qt for Python (Pyside2) Template for Torizon OS
Just as the VSCode Torizon IDE Extension provides a Qt C++ Template, it also provides a ready-to-use Qt5 Pyside2 QML template, with similar benefits in terms of an out-of-the-box experience on Toradex System on Module, application development and integration with other parts of the Torizon OS ecosystem like TorizonCore Builder and Torizon Cloud.
The only caveat is that, unlike the Qt C++ Template, this template does not provide the integration with Qt Creator and Qt Design Studio.
To create and run a Qt for Python application follow the Torizon IDE Extension development workflow.
For now the only Qt for Python template available for Torizon OS is the Qt5 with Pyside2 one, but in the future there will be a Qt for Python template available that uses Qt6.
Executing Qt Containers on CLI (command line interface)
As explained in the Qt Debian Containers for Torizon OS, Toradex provides base containers with Qt base libraries installed and ready to use, with hardware acceleration. The ones that should be used as base for your Qt application are called qt6-wayland, qt6-wayland-vivante and qt6-wayland-am62.
Toradex also provides containers - called qt6-wayland-examples, qt6-wayland-examples-vivante and qt6-wayland-examples-am62- that include qt6-base-examples and offer an out-of-the-box evaluation experience. The following section shows how to run examples within those containers.
There are also the qt5-wayland-examples, qt5-wayland-examples-vivante and qt5-wayland-examples-am62 containers for Qt5, but the following section shows commands for the Qt6 ones.
Run a Weston Container
Connect to the board terminal by establishing an SSH connection.
Start a Weston container which will be the graphics server. Choose your module from the tabs below and follow the instructions:
# docker container run -d --name=weston --net=host \
--cap-add CAP_SYS_TTY_CONFIG \
-v /dev:/dev -v /tmp:/tmp -v /run/udev/:/run/udev/ \
--device-cgroup-rule="c 4:* rmw" --device-cgroup-rule="c 253:* rmw" \
--device-cgroup-rule="c 13:* rmw" --device-cgroup-rule="c 226:* rmw" \
--device-cgroup-rule="c 10:223 rmw" --device-cgroup-rule="c 199:0 rmw" \
torizon/weston-imx8:4 \
--developer
# docker container run -d --name=weston --net=host \
--cap-add CAP_SYS_TTY_CONFIG -v /dev:/dev -v /tmp:/tmp \
-v /run/udev/:/run/udev/ \
--device-cgroup-rule="c 4:* rmw" --device-cgroup-rule="c 13:* rmw" \
--device-cgroup-rule="c 226:* rmw" --device-cgroup-rule="c 10:223 rmw" \
torizon/weston-am62:4 --developer
# docker container run -d --name=weston --net=host \
--cap-add CAP_SYS_TTY_CONFIG -v /dev:/dev -v /tmp:/tmp \
-v /run/udev/:/run/udev/ --device-cgroup-rule="c 4:* rmw" \
--device-cgroup-rule="c 13:* rmw" --device-cgroup-rule="c 226:* rmw" \
--device-cgroup-rule="c 10:223 rmw" \
torizon/weston:4 \
--developer
To learn more about the device_cgroup_rules section of the docker-compose file above, please refer to the Hardware Access through Control Group Rules (cgroup) section of the Torizon Best Practices Guide
Run a Qt Wayland Examples Container
Start a Qt Wayland examples container and run some example application. To do it, select your module from the tabs below and follow the instructions:
- 32-bit SoCs (arm32v7)
- 64-bit SoCs with CPU only (arm64v8)
- 64-bit i.MX 8 SoCs with Vivante graphics acceleration (arm64v8)
- 64-bit AM62 SoCs with graphics acceleration (arm64v8)
The following command brings up the Qt6 Wayland container with an interactive command prompt:
The Qt6 CT Tags are only available on TorizonCore 6.5 and forward.
Therefore, if you are using a version of TorizonCore 6 smaller than that, replace the $CT_TAG_QT6_WAYLAND_EXAMPLES with 3 on the command below.
# docker run --rm -it --name=qt6 \
-v /tmp:/tmp \
-v /dev/dri:/dev/dri --device-cgroup-rule='c 226:* rmw' \
torizon/qt6-wayland-examples:$CT_TAG_QT6_WAYLAND_EXAMPLES \
bash
Use the Qt Quick 2D Renderer
Inside the Qt6 Wayland container, only if you are using a module without GPU (Colibri iMX7 and Colibri iMX6ULL) and plan to also use Qt Quick, we recommend that you use the Qt Quick 2D Renderer, otherwise you may see a poor performance and high CPU load:
only export QMLSCENE_DEVICE=softwarecontext if your module does not have a GPU!
## export QMLSCENE_DEVICE=softwarecontext
Keep in mind that there are feature limitations when using the Qt Quick 2D Renderer.
Start a Qt Sample Application (32-bit SoCs)
Inside the Qt6 Wayland container, start any of the available Qt6 sample applications:
## /usr/lib/arm-linux-gnueabihf/qt6/examples/widgets/widgets/calculator/calculator &
or
## /usr/lib/arm-linux-gnueabihf/qt6/examples/widgets/widgets/shapedclock/shapedclock &
or
## /usr/lib/arm-linux-gnueabihf/qt6/examples/opengl/cube/cube &
or
## /usr/lib/arm-linux-gnueabihf/qt6/examples/opengl/contextinfo/contextinfo &
The following command brings up the Qt6 Wayland container with an interactive command prompt:
The Qt6 CT Tags are only available on TorizonCore 6.5 and forward.
Therefore, if you are using a version of TorizonCore 6 smaller than that, replace the $CT_TAG_QT6_WAYLAND_EXAMPLES with 3 on the command below.
# docker run --rm -it --name=qt6 \
-v /tmp:/tmp \
-v /dev/dri:/dev/dri --device-cgroup-rule='c 226:* rmw' \
torizon/qt6-wayland-examples:$CT_TAG_QT6_WAYLAND_EXAMPLES \
bash
Start a Qt Sample Application (64-bit SoCs with CPU only)
Inside the Qt6 Wayland container, start any of the available Qt6 sample applications:
## /usr/lib/aarch64-linux-gnu/qt6/examples/widgets/widgets/calculator/calculator &
or
## /usr/lib/aarch64-linux-gnu/qt6/examples/widgets/widgets/shapedclock/shapedclock &
or
## /usr/lib/aarch64-linux-gnu/qt6/examples/opengl/cube/cube &
or
## /usr/lib/aarch64-linux-gnu/qt6/examples/opengl/contextinfo/contextinfo &
Please, note that by executing the following line you are accepting the terms and conditions of the NXP's End-User License Agreement (EULA)
The following command brings up the Qt6 Wayland container with an interactive command prompt:
The Qt6 CT Tags are only available on TorizonCore 6.5 and forward.
Therefore, if you are using a version of TorizonCore 6 smaller than that, replace the $CT_TAG_QT6_WAYLAND_EXAMPLES with 3 on the command below.
# docker run -e ACCEPT_FSL_EULA=1 --rm -it --name=qt6 \
-v /tmp:/tmp \
-v /dev/dri:/dev/dri -v /dev/galcore:/dev/galcore \
--device-cgroup-rule='c 199:* rmw' --device-cgroup-rule='c 226:* rmw' \
torizon/qt6-wayland-examples-vivante:$CT_TAG_QT6_WAYLAND_EXAMPLES_VIVANTE \
bash
Start a Qt Sample Application (64-bit i.MX 8 SoCs with Vivante graphics acceleration)
Inside the Qt6 Wayland container, start any of the available Qt6 sample applications:
## /usr/lib/aarch64-linux-gnu/qt6/examples/widgets/widgets/calculator/calculator &
or
## /usr/lib/aarch64-linux-gnu/qt6/examples/widgets/widgets/shapedclock/shapedclock &
or
## /usr/lib/aarch64-linux-gnu/qt6/examples/opengl/cube/cube &
or
## /usr/lib/aarch64-linux-gnu/qt6/examples/opengl/contextinfo/contextinfo &
The following command brings up the Qt6 Wayland container with an interactive command prompt:
The Qt6 CT Tags are only available on TorizonCore 6.5 and forward.
Therefore, if you are using a version of TorizonCore 6 smaller than that, replace the $CT_TAG_QT6_WAYLAND_EXAMPLES with 3 on the command below.
# docker run --rm -it --name=qt6 \
-v /tmp:/tmp \
-v /dev/dri:/dev/dri \
--device-cgroup-rule='c 226:* rmw' \
torizon/qt6-wayland-examples-am62:$CT_TAG_QT6_WAYLAND_EXAMPLES \
bash
Start a Qt Sample Application (64-bit AM62 SoCs with graphics acceleration)
Inside the Qt6 Wayland container, start any of the available Qt6 sample applications:
## /usr/lib/aarch64-linux-gnu/qt6/examples/widgets/widgets/calculator/calculator &
or
## /usr/lib/aarch64-linux-gnu/qt6/examples/widgets/widgets/shapedclock/shapedclock &
or
## /usr/lib/aarch64-linux-gnu/qt6/examples/opengl/cube/cube &
or
## /usr/lib/aarch64-linux-gnu/qt6/examples/opengl/contextinfo/contextinfo &